|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
The EU AI Act which has just come into effect is making headlines in the AI world this week. This Regulation has potentially huge implications for organizations globally, so we will ensure you are covered on all fronts and ready.
Here’s everything you need to know to safeguard your AI journey and remain compliant.
What is the EU AI Act?
The EU AI Act is a groundbreaking piece of legislation designed to regulate the development and use of artificial intelligence within the European Union.
This pioneering legislation aims to regulate AI systems based on their perceived risk levels. This law seeks to establish a robust framework for innovation, development, deployment, and use of AI, ensuring that it aligns with fundamental rights and values.
As the world’s first comprehensive AI regulation, the EU is setting a global precedent for AI governance and has far-reaching implications for organizations operating within or interacting with the EU market. Further, it is likely to influence regulations worldwide, as other countries adopt similar standards to ensure the safe and ethical development of AI.
Who is Affected?
The AI Act has set out clear definitions for the different actors involved in AI:
- AI Developers and Providers: Companies developing and providing AI systems, both within and outside the EU, are directly affected.
- AI Deployers: Organizations using AI systems, regardless of where they were developed, are subject to the Act if the AI output is used within the EU.
- Importers and Distributors: Those involved in bringing AI systems into the EU market must comply with the Act.
- Product Manufacturers: Companies producing products containing AI components fall under the Act’s purview.
Essentially, anyone involved in the development, deployment, or use of AI systems within the EU or targeting the EU market is affected by the AI Act and will be held accountable. This also means, your organization doesn’t need to be physically present in the EU for its business parts to fall under this legislation.
A Risk-Based Approach
The EU AI Act adopts a risk-based approach to regulating AI, meaning the level of regulation depends on the potential harm an AI system could cause.
The EU AI Act categorizes AI systems into four risk tiers:
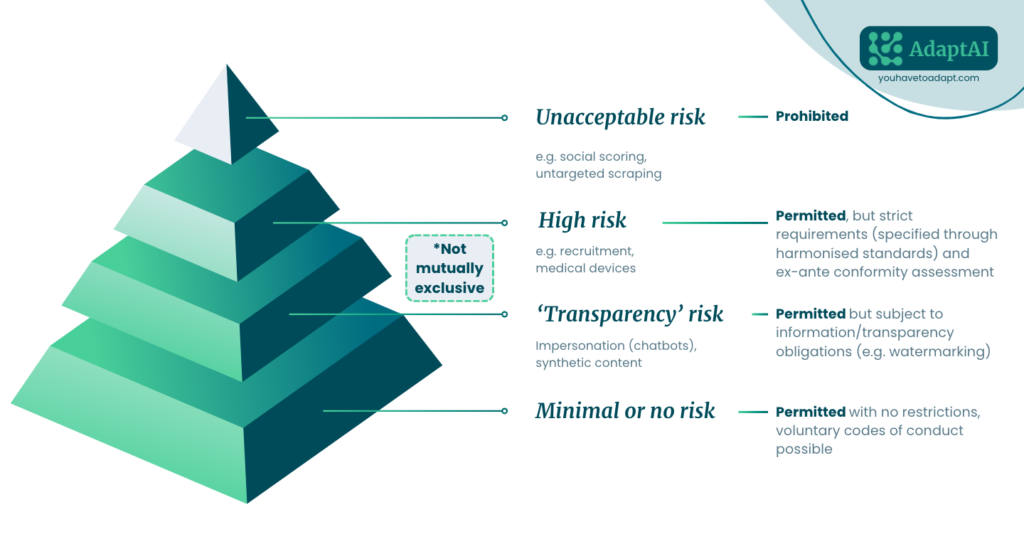
- Unacceptable risk AI is outright banned, including systems that manipulate human behavior to exploit vulnerabilities or social scoring systems.
- High-risk AI systems, such as those used in critical infrastructure, education, employment, law enforcement, and border control, are subject to stringent requirements. These include robust risk assessments, data quality assurance, transparency, human oversight, record-keeping, and cybersecurity measures.
- Low-risk AI systems, like chatbots or spam filters, will undergo less stringent obligations but still need to comply with general safety and transparency rules.
- Minimal-risk AI systems, such as AI-powered video games, are largely exempt from regulation.
Subscribe to AI Pulse
Your new guide to the best and latest insights on AI adoption and holistic digital transformation each Friday – from the AdaptAI team.
EU AI Act Timeline
Over the next few years, organizations will face staggered deadlines:
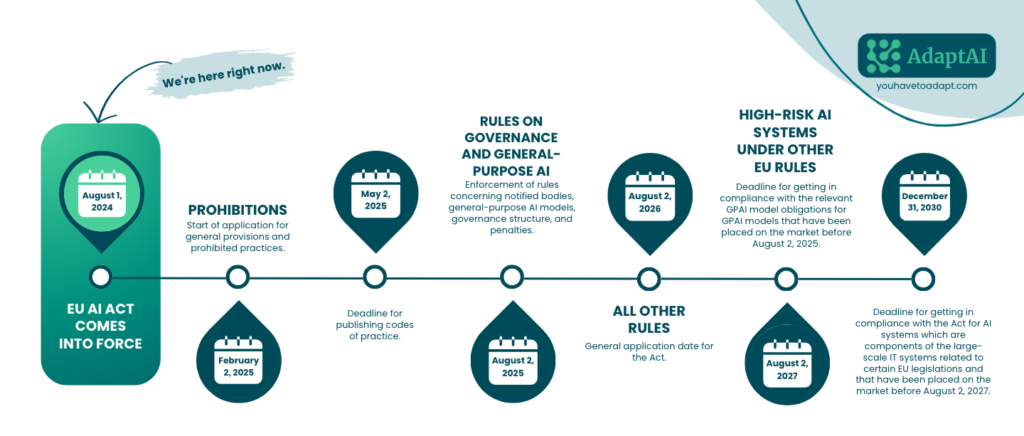
The first phase “Prohibitions of Certain AI Systems,“ effective February 2025, will outright ban specific AI applications. These include systems that exploit personal vulnerabilities like health or financial data, as well as those that unlawfully collect facial images from public spaces or create facial recognition databases.
A practical example: AI systems will not be allowed to use personal health data to target individuals for specific medical products or services.
Starting in August 2025, companies offering versatile AI systems capable of performing a wide range of tasks, known as general-purpose AI models (GPAI), will be required by the new law to disclose detailed information about the data used to train these systems to the public. Unlike specialized AI systems designed for specific purposes like image recognition, general-purpose AI models are adaptable tools with multiple applications. Generative AI tools, like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google’s Gemini or Meta’s Llama, for example, fall into this category.

As of 2 August 2026, the remainder of the AI Act starts to apply, except Article 6. This means that EU AI Act applies “to operators of high-risk AI systems (other than those systems referred to in Article 111(1)), placed on the market or put into service before this date. However, this only applies to systems which are subject to significant changes in their designs from this date onwards.“
Further, by 2 August 2027, providers of GPAI models placed on the market before 2 August 2025 must have taken the necessary steps to comply with the obligations laid down in the EU AI Act. Finally, AI systems which are components of large-scale IT systems and that were placed on the market or put into service before 2 August 2027 need to be compliant with the EU AI Act by the end of 2030.
All organizations will have to react quickly and start adapting to these fast-approaching new regulations, or else they risk facing heavy fines for noncompliance.
*SMEs Consideration: Fines are capped at the lower of specified percentages or amounts for SMEs to prevent disproportionate burdens.
A Practical Example: HR Department
Let’s consider a hypothetical HR department using AI for recruitment.
AI-powered chatbot for initial applicant screening: This system could provide basic information about the company and answer frequently asked questions. As it doesn’t directly impact employment decisions, it’s likely to be considered low risk.
Implications: While not heavily regulated, transparency is key. Inform applicants they are interacting with a chatbot and ensure the chatbot provides accurate and non-discriminatory information.
AI-powered tool for resume screening and shortlisting candidates: This system directly impacts employment opportunities and could potentially lead to discriminatory outcomes.
Implications: Under the EU AI Act, this would be considered a high-risk application. HR departments would need to:
- Conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential biases.
- Ensure data quality and accuracy.
- Implement robust human oversight and explainability mechanisms.
- Be prepared to provide detailed documentation of the AI system and its decision-making processes.
Lead your team towards success!
Our in-depth sessions and people-oriented interventions are designed to ensure a swift AI adoption across your enterprise.
What Steps Should Businesses Be Taking?
There is a pressing need for organizations to prepare for the upcoming regulations as part of the EU AI Act. Some experts suggest at best a couple of months to get all things in order within smaller organizations, however, if you think of large-scale enterprises with a global AI footprint then the timeframe suddenly gets considerably shorter.
To get you up to speed, here are the steps you should be considering taking:
The initial step involves identifying which regulations will impact the business. The new AI Act categorizes companies into distinct roles: deployers, providers, and importers, each with its own compliance obligations. Determining the company’s exact role within this framework is crucial.
For instance, is the company acquiring pre-trained models and deploying them with minimal modifications, or is it heavily customizing these models to fit specific use cases? The answers to these questions will shape the compliance strategy.
Once a company understands its regulatory landscape, it must conduct a comprehensive inventory of its AI systems. This involves not only identifying AI systems currently in production and development but also understanding their functions, data inputs, outputs, and intended use cases.
To conduct a thorough risk assessment, organizations must consider the potential impact of these systems on individuals, society, and the environment. Such an inventory will provide a clear picture of the AI landscape within the organization, enabling a more targeted risk assessment.
A critical aspect of this assessment is determining the potential harm that could arise from these AI systems. This involves evaluating factors such as the system's complexity, the sensitivity of the data it processes, and the potential consequences of errors or biases. By understanding the potential risks, organizations can prioritize mitigation strategies and allocate resources effectively.
Many organizations lack a clear overview of their AI landscape, making this assessment a critical starting point. Consider using the EU AI Act Compliance Checker which can help you identify and assess the compliance status of their AI systems, ensuring alignment with regulatory requirements.
To ensure ongoing compliance, organizations must establish robust processes for new AI system development and deployment. These processes should be designed to proactively integrate regulatory requirements from the outset, rather than attempting to retrofit compliance after the fact. This proactive approach is more efficient and less disruptive to operations.
To achieve this, organizations should consider implementing the following steps:
- Develop a comprehensive AI governance framework that outlines roles and responsibilities, decision-making processes, and accountability mechanisms.
- Establish clear guidelines for the development and deployment of AI systems, including requirements for risk assessment, data privacy, and ethical considerations.
- Integrate AI compliance into the software development lifecycle (SDLC) to ensure that regulatory requirements are considered throughout the development process.
- Provide adequate training and resources to employees involved in AI development and deployment to ensure they understand their obligations and responsibilities.
- Continuous monitoring and evaluation: Regularly assess the effectiveness of AI governance practices and make necessary adjustments to stay ahead of emerging challenges.
Please keep in mind that the EU AI Act is complex, and the regulatory landscape is still evolving. It's crucial to stay informed and seek professional advice to ensure compliance.
Successful AI governance demands a strategic approach that involves the C-suite. A multidisciplinary team, including technical experts and privacy professionals, is essential to navigate the complexities of AI regulation.
To achieve this, organizations should consider the following:
- C-suite involvement: Ensure that senior leadership understands the importance of AI governance and actively participates in decision-making processes.
- Cross-functional collaboration: Establish a dedicated AI governance team that brings together representatives from various departments, including legal, compliance, risk management, IT, and business operations.
- Culture of compliance: Foster a culture of AI ethics and responsibility throughout the organization, emphasizing the importance of transparency, accountability, and fairness.
However, ultimate responsibility and direction should reside at the highest levels of the organization. This ensures alignment with overall business objectives and effective risk management.
The initial step involves identifying which regulations will impact the business. The new AI Act categorizes companies into distinct roles: deployers, providers, and importers, each with its own compliance obligations. Determining the company’s exact role within this framework is crucial.
For instance, is the company acquiring pre-trained models and deploying them with minimal modifications, or is it heavily customizing these models to fit specific use cases? The answers to these questions will shape the compliance strategy.
Once a company understands its regulatory landscape, it must conduct a comprehensive inventory of its AI systems. This involves not only identifying AI systems currently in production and development but also understanding their functions, data inputs, outputs, and intended use cases.
To conduct a thorough risk assessment, organizations must consider the potential impact of these systems on individuals, society, and the environment. Such an inventory will provide a clear picture of the AI landscape within the organization, enabling a more targeted risk assessment.
A critical aspect of this assessment is determining the potential harm that could arise from these AI systems. This involves evaluating factors such as the system’s complexity, the sensitivity of the data it processes, and the potential consequences of errors or biases. By understanding the potential risks, organizations can prioritize mitigation strategies and allocate resources effectively.
Many organizations lack a clear overview of their AI landscape, making this assessment a critical starting point. Consider using the EU AI Act Compliance Checker which can help you identify and assess the compliance status of their AI systems, ensuring alignment with regulatory requirements.
To ensure ongoing compliance, organizations must establish robust processes for new AI system development and deployment. These processes should be designed to proactively integrate regulatory requirements from the outset, rather than attempting to retrofit compliance after the fact. This proactive approach is more efficient and less disruptive to operations.
To achieve this, organizations should consider implementing the following steps:
- Develop a comprehensive AI governance framework that outlines roles and responsibilities, decision-making processes, and accountability mechanisms.
- Establish clear guidelines for the development and deployment of AI systems, including requirements for risk assessment, data privacy, and ethical considerations.
- Integrate AI compliance into the software development lifecycle (SDLC) to ensure that regulatory requirements are considered throughout the development process.
- Provide adequate training and resources to employees involved in AI development and deployment to ensure they understand their obligations and responsibilities.
- Continuous monitoring and evaluation: Regularly assess the effectiveness of AI governance practices and make necessary adjustments to stay ahead of emerging challenges.
Please keep in mind that the EU AI Act is complex, and the regulatory landscape is still evolving. It’s crucial to stay informed and seek professional advice to ensure compliance.
Successful AI governance demands a strategic approach that involves the C-suite. A multidisciplinary team, including technical experts and privacy professionals, is essential to navigate the complexities of AI regulation.
To achieve this, organizations should consider the following:
- C-suite involvement: Ensure that senior leadership understands the importance of AI governance and actively participates in decision-making processes.
- Cross-functional collaboration: Establish a dedicated AI governance team that brings together representatives from various departments, including legal, compliance, risk management, IT, and business operations.
- Culture of compliance: Foster a culture of AI ethics and responsibility throughout the organization, emphasizing the importance of transparency, accountability, and fairness.
However, ultimate responsibility and direction should reside at the highest levels of the organization. This ensures alignment with overall business objectives and effective risk management.
How Can AdaptAI Help Your Business?
The AI landscape is undeniably complex, and regulations like the EU AI Act introduce a new pieces of the puzzle for businesses to navigate. It’s easy to feel overwhelmed by the sheer volume of information and the potential consequences of non-compliance or even not introducing AI to your business on time.
The key to success lies in strategic approach and proactive action. While we are not an AI governance service provider, we understand the challenges businesses face in navigating this new territory.
Cutting through the noise, we provide businesses with deep expertise in strategic innovation and people-centered transformation, along with recommendations on the most relevant tools for their needs.
You can rely on us for:
- Tailored and light workshop sessions, designed to provide you with a focused introduction to the key aspects of AI, providing practical insights and actionable steps.
- For a more comprehensive approach, our holistic digital transformation services can help you embed AI into your core business processes and help you innovate. By combining technology, strategy, and people development, we can guide you towards a future where AI is not just compliant but a strategic advantage.
Understanding and adapting to these new technological changes is not merely a box-ticking exercise; it’s an opportunity to build trust, enhance reputation, and gain a competitive edge.
Together, we can ensure your AI initiatives drive a positive change.




